그래프를 탐색하는 방법에는 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)과 너비 우선 탬색(BFS)가 있습니다.
1. 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)
Root Node 혹은 다른 임의의 Node에서 최대한 깊이 내려간 뒤, 더 이상 깊이 갈 곳이 없을 경우 옆 Branch로 이동하는 탐색 방법입니다.
즉, 해당 분기를 완벽하게 탐색하는 방법입니다.
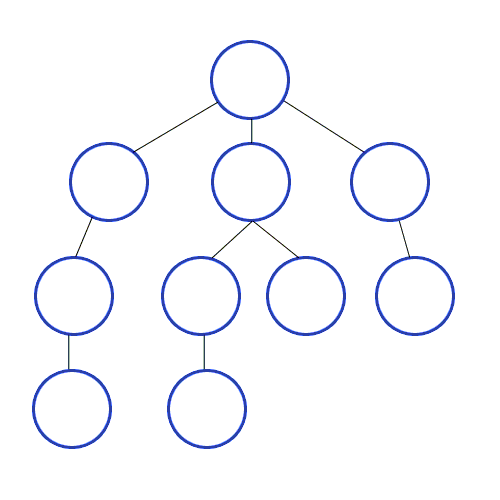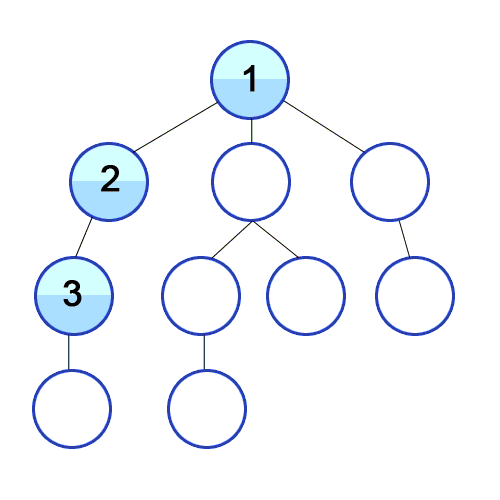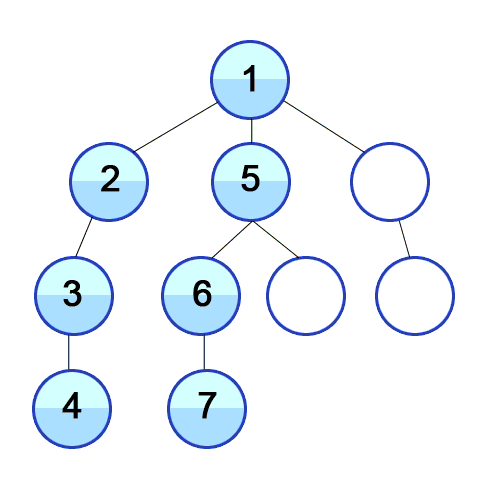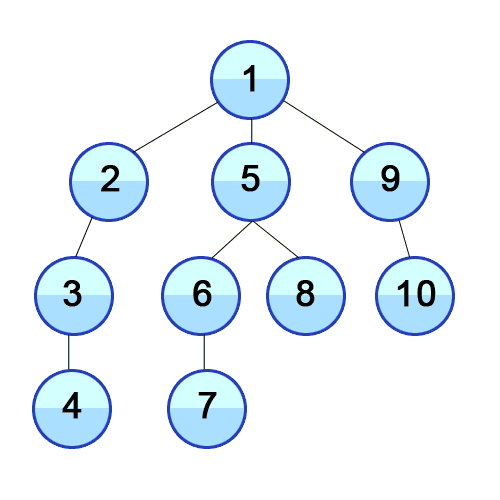
특징
- 모든 노드를 방문하고자 하는 경우(완전 탐색)
- 미로 찾기, 퍼즐 문제
- 검색 속도는 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)에 비해서 느림
- 모든 경로를 한 번에 탐색하지 않기 때문에 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)보다 메모리 사용량이 적을 수 있음
Java 코드 (Stack을 사용해서 구현)
class Graph {
private int V; // Number of vertices
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[]; // Adjacency list
// Constructor
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v's list
}
// DFS traversal of the vertices reachable from v
void DFS(int v) {
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (set as false by default)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// Push the current source node
stack.push(v);
while (!stack.empty()) {
// Pop a vertex from stack and print it
v = stack.pop();
// Stack may contain the same vertex twice. So we need to print the popped item only if it is not visited.
if (!visited[v]) {
System.out.print(v + " ");
visited[v] = true;
}
// Get all adjacent vertices of the popped vertex v
// If an adjacent has not been visited, then push it to the stack
Iterator<Integer> itr = adj[v].iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
int adjVertex = itr.next();
if (!visited[adjVertex])
stack.push(adjVertex);
}
}
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void main(String args[]) {
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
System.out.println("Following is Depth First Traversal " +
"(starting from vertex 2)");
g.DFS(2);
}
}
2. 너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
Root Node 혹은 다른 임의의 Node에서 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방법입니다. 최대한 같은 레벨의 노드로 이동한 다음 더 이상 없을 경우 아래로 이동합니다.
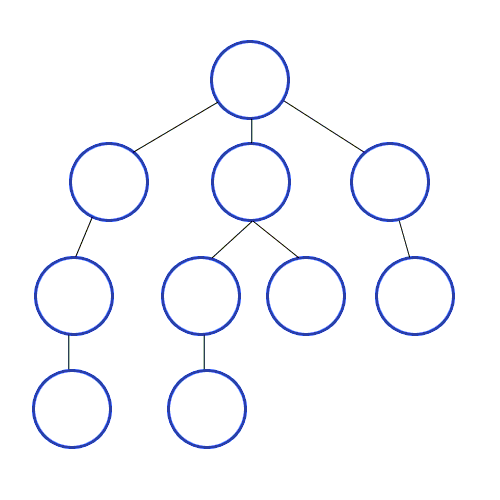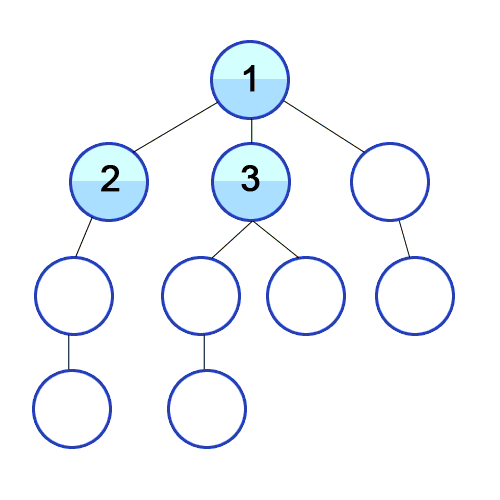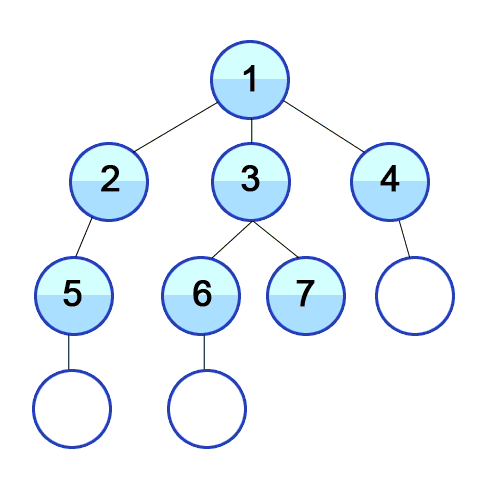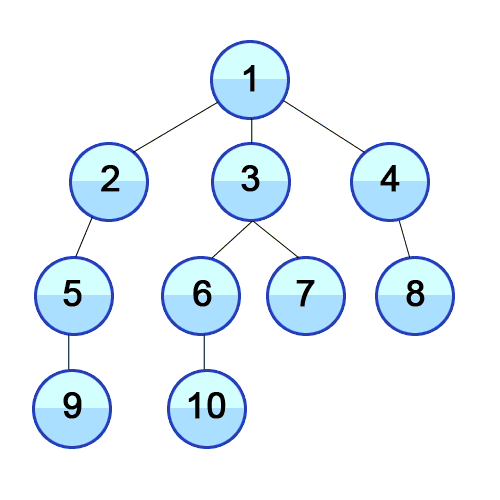
특징
- 두 노드 사이의 최단 경로를 찾고 싶을 때 사용
- 길 찾기, 특정 사용자의 친구 찾기, 웹 크롤러
- 주로 FIFO구조를 사용 (Queue)
- 방문해야 할 모든 Node를 큐에 저장하기 때문에, DFS보다 메모리 사용량이 많을 수 있음
Java 코드 (Queue을 사용해서 구현)
class Graph {
private int V; // Number of vertices
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[]; // Adjacency list
// Constructor
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w); // Add w to v's list
}
// BFS traversal from a given source s
void BFS(int s) {
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (by default set as false)
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
// Create a queue for BFS
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.add(s);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
s = queue.poll();
System.out.print(s + " ");
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s
// If an adjacent has not been visited, then mark it visited and enqueue it
Iterator<Integer> itr = adj[s].iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
int n = itr.next();
if (!visited[n]) {
visited[n] = true;
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
}
// Driver method to test above
public static void main(String args[]) {
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
System.out.println("Following is Breadth First Traversal " +
"(starting from vertex 2)");
g.BFS(2);
}
}
연관 문제
[공통]
DFS와 BFS : https://developer-mac.tistory.com/63
연결 요소 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11724
이분 그래프 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1707
섬의 개수 : https://developer-mac.tistory.com/66
단지번호 붙이기 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2667
섬의 개수 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/4963
[BFS]
토마토 1 : https://developer-mac.tistory.com/67
토마토 2 : https://developer-mac.tistory.com/68
참고
[코딩테스트 대비] DFS, BFS 정리
DFS, BFS 정리 DFS, BFS는 그래프에 속하는 알고리즘이다. 코딩테스트에서 경로를 찾는 문제에서 많이 출제가 된다. DFSRoot Node 혹은 다른 임의의 Node에서 다음 분기(Branch)로 넘어가기 전에 해당 분기
developer-mac.tistory.com